Coffee and antioxidants: Everything you need to know.
|
|
Time to read 5 min
Order for more €39 for Free shipping!
|
|
Time to read 5 min
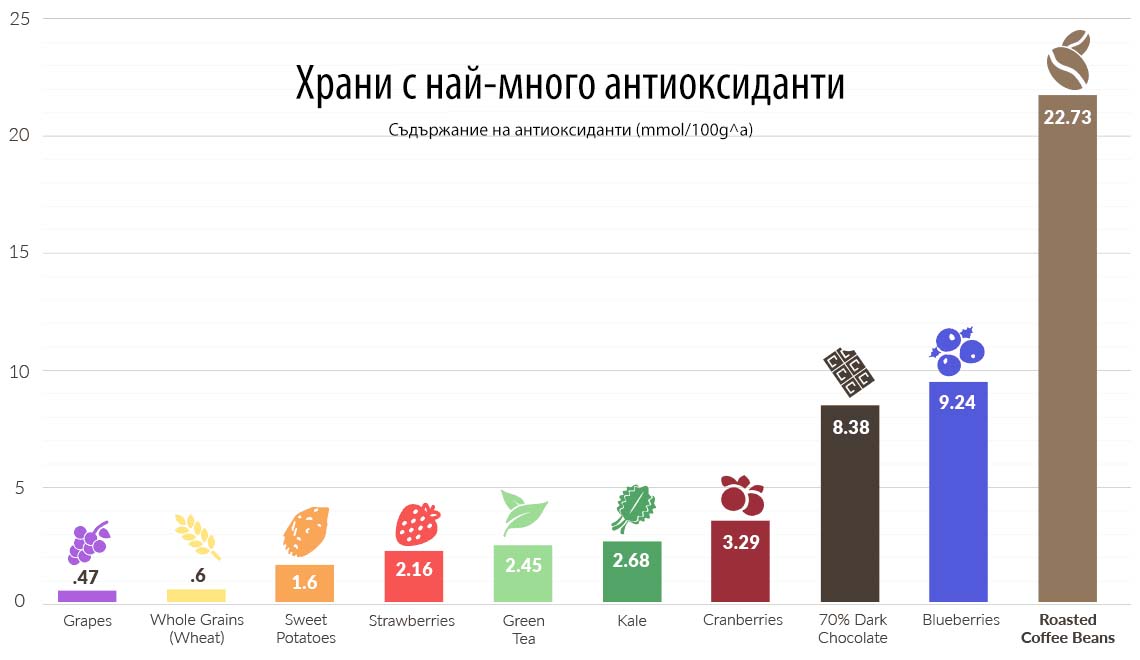
Coffee contains antioxidants like phenolic acids and flavonoids, which may help protect against chronic diseases like diabetes, Alzheimer's disease, and some types of cancer.
Coffee is one of the most popular beverages in the world, with approximately 400 million cups consumed daily.
Research shows that regular coffee drinking may play a role in preventing chronic diseases and improving body condition.
This may be due to the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of coffee.
Antioxidants are compounds that help protect the body from free radicals. Free radicals are atoms that attack the body and cause oxidative stress, which can damage important molecules like proteins and DNA.
A 2022 study isolated more than 136 bioactive compounds in coffee, most of which are antioxidants.
Phenolic acids make up the largest portion of antioxidants in coffee, followed by flavonoids.
Coffee contains over 100 polyphenols, which are antioxidant compounds such as phenolic acids and flavonoids.
They may help protect against oxidative stress, which can lead to neurodegenerative and chronic conditions such as obesity, cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Researchers have identified 38 phenolic acids in coffee, with chlorogenic acids being the most common. Phenolic acids may contribute the most to coffee's ability to fight free radicals and protect against oxidative stress.
A 2022 study found that coffee derivatives like hydrocinnamic acid may prevent neurodegeneration in the brain, which can lead to conditions like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases.
The authors note that hydrocinnamic acid may prevent the transformation of certain proteins into amyloid plaques in the brain. These plaques are one of the main characteristics of Alzheimer's disease.

Flavonoids are a type of polyphenol found in plants. There are nearly 10,000 flavonoid metabolites, many of which may help fight oxidative stress and inflammation.
Researchers have identified about 41 flavonoids in coffee, including:
Catechins are an important flavonoid in coffee, especially epicatechin gallate (EGG) and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). They may help protect against mitochondrial disease.
Mitochondria help produce energy for the cells in your body. EGC and EGCG may help regulate mitochondria, fight oxidative damage, and improve insulin resistance, all factors that can contribute to chronic disease.
Finally, caffeine, which is mostly recognized as a stimulant, may have antioxidant properties that can help protect against oxidative damage and inflammation associated with:
Some research suggests that the antioxidants in coffee may contribute to weight loss.
A small study from 2024 examined the effects of drinking coffee with varying levels of antioxidants such as caffeine and hydroxycinnamic acids.
After 6 weeks, participants who consumed 3 cups of coffee daily with higher levels of antioxidants had greater reductions in body fat percentage, body weight, and fat mass.
Learn more about coffee and weight loss.

There is no clear answer when it comes to the best type of coffee for antioxidants. The concentration, types, and role of antioxidants in coffee can vary widely depending on factors such as:
A 2021 study examined the amount of antioxidants in espresso, instant coffee, and Americano.
The researchers found that espresso contained 6.23 milligrams per milliliter (mg/mL) of melanoidins, and instant coffee contained 5.78 mg/mL. However, Americano contained only 0.71 mg/mL.
When evaluating chlorogenic acids per 100 ml, espresso contains the highest amount, 158.31 mg/100 ml, and Americano the lowest, 17.69 mg/mL.
A 2019 study looked at antioxidants in coffee beans from four different countries. Researchers found that Colombian coffee had the highest levels of total polyphenols, followed by coffee from Ethiopia, Australia, and Peru.
A 2020 study examined antioxidant levels in coffee beans that were organic or conventional, roasted at different temperatures, and brewed for 3 or 6 minutes.
Researchers found that organic coffee contains more phenolic acids — such as chlorogenic, caffeic, and salicylic — than regular coffee, but contains less caffeine. The levels of flavonoids are very similar between the two types.
They also found that medium-roasted coffee had more phenolic acids, caffeine, and antioxidant activity compared to light or dark roasted coffee.
However, dark roasted coffee has significantly higher levels of salicylic acid, and light roasted coffee has higher levels of flavonoids.
A shorter brewing time of 3 minutes yields a higher number of phenolic acids, while a 6-minute brewing time is better for flavonoids.
The researchers concluded that organic coffee beans, a medium roast, and a 3-minute brew may be the best factors for maximizing antioxidant activity. However, regular beans may provide more caffeine and flavonoids.
Order a coffee machine from REMACAFFE now.
Coffee in REMACAFFE capsules retains its beneficial substances for the longest time, due to the fact that it is packaged entirely in a nitrogen environment, and oxygen, which can oxidize the coffee, is completely absent.
There are several ways to prepare your coffee, and all of them can provide some antioxidant benefits.
A 2021 study examined the polyphenol concentration and antioxidant effects of three different coffee brewing methods, including espresso, instant, and Americano.
The researchers found that espresso contained the highest amount of polyphenols and caffeine, but instant coffee had significantly less of them. Americano also had lower amounts.
A 2022 study also found that filtered coffee may provide several bioactive compounds.
Research on how much coffee you should drink daily to experience antioxidant benefits varies widely and may depend on your goal. For example:
A 2017 review found that drinking 1 to 3 cups of coffee daily was associated with a lower risk of hypertension and hyperhomocysteinemia.
A 2016 study found that the risk of colorectal cancer decreased by 7% for every 4 cups of coffee consumed daily.
A 2022 review found that people with Parkinson's disease who consumed at least 200 mg of caffeine daily for 6 weeks experienced improvements in motor function and disease progression.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommends consuming no more than 400 mg of caffeine per day. That's the equivalent of two to three 12-ounce cups of coffee.
There are many types of dietary antioxidants, and coffee is a very good source of some of them. However, it does not provide the same antioxidants as whole plant foods like fruits and vegetables.
To benefit from the antioxidants in coffee, enjoy it as part of a well-balanced diet.